Fuel management
Fuel management refers to the process of effectively managing and optimizing fuel consumption in various industries, such as transportation, logistics, fleet management, and manufacturing. Efficient fuel management strategies can help reduce costs, improve operational efficiency, and minimize environmental impact. Here are some key aspects of fuel management:
Monitoring and Tracking
-
- Fuel consumption tracking: Utilize technologies such as telematics, fuel monitoring systems, or onboard sensors to track and monitor fuel consumption in real time. This provides insights into fuel usage patterns, efficiency, and potential areas for improvement.
- Vehicle tracking: Implement GPS or fleet management systems to track vehicle locations and routes. This allows for efficient routing, reducing unnecessary mileage and fuel consumption.


Driver Training and Behavior
-
- Efficient driving techniques: Provide driver training programs focused on fuel-efficient driving techniques, such as smooth acceleration and deceleration, avoiding excessive idling, and maintaining steady speeds.
- Driver behavior monitoring: Use telematics systems or driver scorecards to monitor driver behavior and provide feedback to promote fuel-efficient driving practices. Recognize and reward drivers who consistently demonstrate efficient driving habits.
Fuel Purchase and Pricing
- Fuel sourcing and contracts: Explore options for fuel sourcing, such as negotiating long-term contracts or utilizing fuel cards with discounted rates, to optimize fuel purchasing and minimize costs.
- Price monitoring: Keep track of fuel prices in different locations and take advantage of lower-cost fuel stations along routes or at strategic locations.

Route Optimization
-
- Efficient route planning: Utilize advanced route planning software or GPS systems to optimize routes and minimize mileage. This helps reduce fuel consumption by identifying the most direct and time-efficient routes.
- Traffic and congestion avoidance: Monitor traffic conditions in real time and reroute vehicles to avoid heavy congestion or roadblocks. This minimizes unnecessary fuel consumption due to idling in traffic.
Fuel log
By implementing effective fuel management practices, businesses can optimize fuel consumption, reduce costs, and promote sustainability. Regular monitoring, driver training, efficient maintenance, route optimization, and strategic fuel purchasing contribute to improved fuel efficiency and overall operational performance.
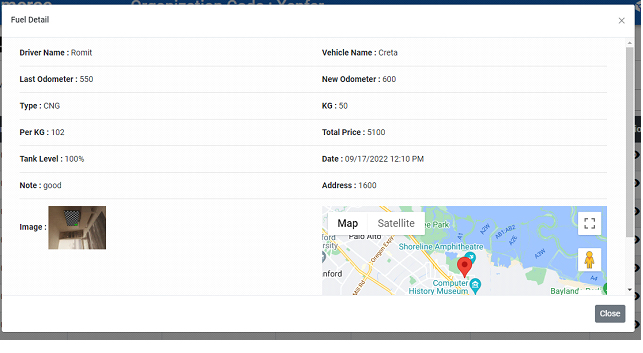
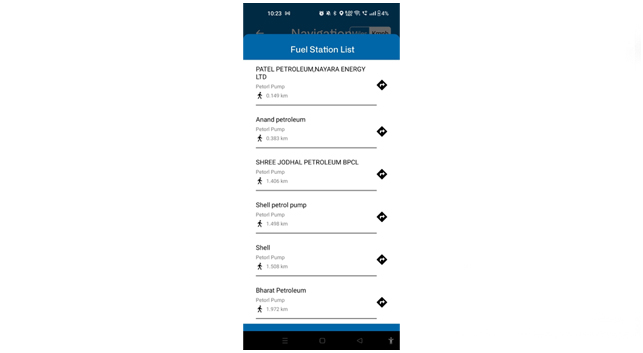
Fuel and maintenance stops
Fuel and maintenance stops: Plan for refueling and maintenance stops along the route to keep vehicles in optimal condition and minimize downtime.
Efficient Vehicle Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance: Implement a proactive maintenance program to ensure vehicles are properly maintained, including regular engine tune-ups, tire maintenance, and fluid checks. Well-maintained vehicles operate more efficiently and consume less fuel.
- Proper tire inflation: Monitor and maintain proper tire pressure, as underinflated tires can significantly increase fuel consumption. Regularly inspect and inflate tires to the manufacturer’s recommended pressure levels.



